Alfalfa mosaic virus Alfamovirus Bromoviridae Unassigned single stranded positivesense RNA viruses Singlestranded, positivesense, RNA (Group IV) 44 alternanthera mosaic virus (AltMV) AltMV Potexvirus Group VI viruses can integrate this doublestranded DNA into the host genome The Group VI viruses are referred to as retroviruses The Group V viruses, like the Group VI viruses, are singlestranded negative sense RNA virusesRNA viruses are viruses with RNA in their genomes These viruses can be further classified as singlestranded RNA viruses and doublestranded RNA viruses
Rna Virus Replication Transcription Viralzone
Double stranded rna virus example
Double stranded rna virus example- RNA is singlestranded and DNA is double stranded Therefore, reverse transcriptase convert single stranded to double stranded Reverse transcriptase is isolated from retroviruses which means RNA viruses Reverse Transcriptase Example 1 Retrovirus such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is associated with diseases such as acquired rabies virus (rhabdovirus) Doublestranded RNA viruses The virion (genomic) RNA is double stranded and so cannot function as mRNA;




Rna Virus Wikipedia
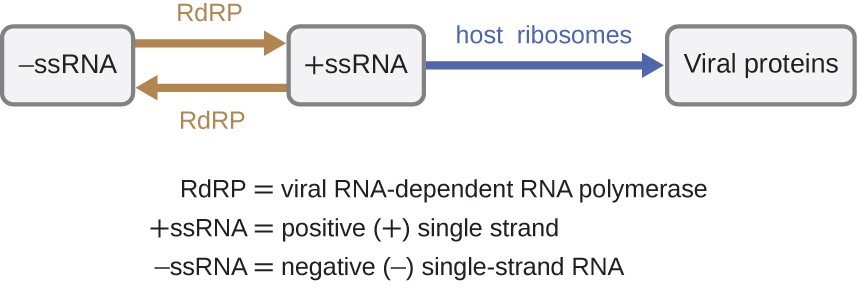
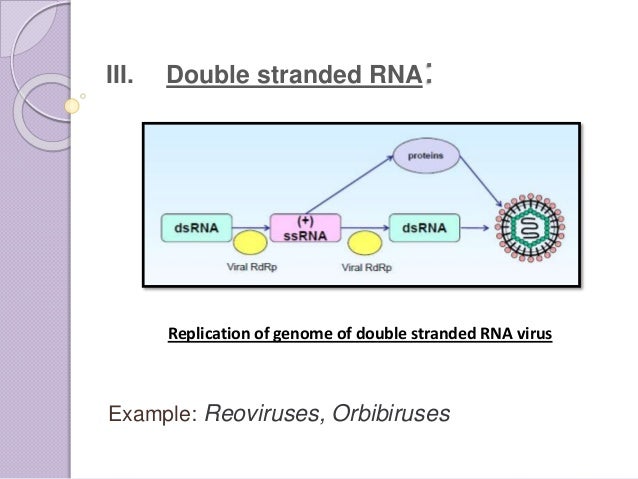
As expected, within each class, viruses share structural similarities;And the Ebola virus are singlestranded RNA viruses Rotaviruses, which cause severe gastroenteritis in children and other immunocompromised individuals, are examples of doublestranded 3 Group III doublestranded RNA viruses Viruses of this group contain doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) After entering the host body the RNAdependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) transcribed the dsRNA genome into mRNA, later this transcribed mRNA is used for the translation or replication Example of Group III Viruses Reoviridae and Birnaviridae 4
Thus these viruses also need to package an RNA polymerase to make their mRNA after infection of the host cell Example rotaviruses (belong to reovirus family) RNA viruses that copy their RNA to DNADNA virus A virus in which the genetic material is DNA rather than RNA The DNA may be either double or singlestranded Major groups of doublestranded DNA viruses (class I viruses) include the adenoviruses, the herpes viruses, and the poxvirusesThe doublestranded (ds)RNA viruses represent a diverse group of viruses that vary widely in host range (humans, animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria), genome segment number (one to twelve), and virion organization (Tnumber, capsid layers, or turrets) Members of this fascinating group include the rotaviruses, renowned globally as the
Viruses can be differentiated based on how they store their genomic information, such as by DNA or doublestranded RNA Positivesense singlestranded RNA (ssRNA) viruses are one such way and it is a key aspect of the infectious cycle of the virus Two important examples of ssRNA viruses are SARSCoV2 and Hepatovirus A, which causeRNA viruses represent a large and important group of pathogens that infect a broad range of hosts Segmented RNA viruses are a subclass of this group that encode their genomes in two or more molecules and package all of their RNA segments in a single virus particle These divided genomes come in different forms, including doublestranded RNA, codingsense singlestranded RNA,The dsRNA viruses represent a large, diverse group of pathogens (affecting a very wide range of host species), several of which are of medical, veterinary or agricultural importance Many of the icosahedral dsRNA viruses show striking structural and




Which Viruses Have Single Stranded Rna That Acts As A Template For Dna Synthesis Study Com
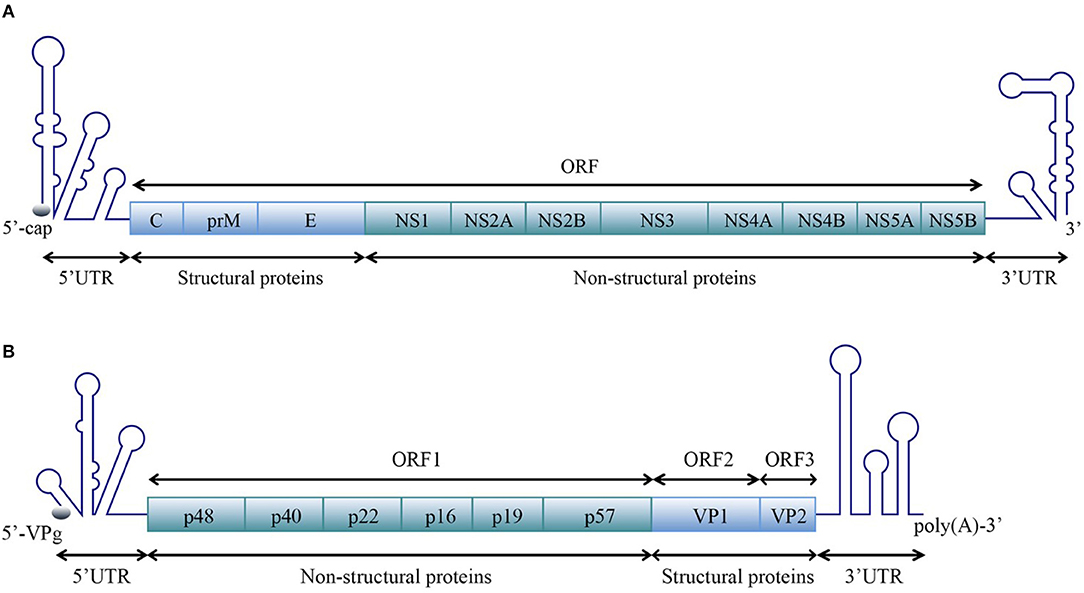



Frontiers Structures And Functions Of The 3 Untranslated Regions Of Positive Sense Single Stranded Rna Viruses Infecting Humans And Animals Cellular And Infection Microbiology
Example of viruses classified by caspid design Viruses are classified based on their core genetic material and capsid design (a) Rabies virus has a singlestranded RNA (ssRNA) core and an enveloped helical capsid, whereas (b) variola virus, the causative agent of smallpox, has a doublestranded DNA (dsDNA) core and a complex capsidBut there are no properties, other than the defining property of a ()sense single stranded RNA genome, that extends to all six classes of the Group IV viruses For example, some classes have envelopes (ie, Flaviviridae, Togaviridae, Coronaviridae), and others do not (ieAnswer (1 of 2) here are many viruses with a doublestranded DNA genome that are known to infect mammals They are subdivided into seven virus families Hepadnaviridae, Polyomaviridae, Papillomaviridae, Adenoviridae, Herpesviridae, Poxviridae




Development Of Nucleic Acid Vaccines Use Of Self Amplifying Rna In Li Ijn




Rna To The Rescue Rna Is One Of The Most Promising Targets For Drug Development Given Its Wide Variety Of Uses Embo Reports Vol 21 No 7
The replication cycle of double stranded RNA viruses are faster than single stranded RNA viruses Double stranded RNA viruses unlike DNA viruses can replicated in the cytosol Rabies, a slowmoving virus, is an example of a double stranded RNA virus A doublestranded RNA virus must produce it own unique viral RNA dependent RNA polymerasePositive strands of RNA generated from negative strand of double strand using viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase positive strands act as mRNA translated in ribosomesRetroviruses use reverse transcriptase to transform their singlestranded RNA into doublestranded DNA It is DNA that stores the genome of human cells and cells from other higher life forms Once transformed from RNA to DNA, the viral DNA can be



Difference Between Positive And Negative Sense Rna Virus Definition Protein Synthesis Replication And Differences




22 The Viruses Biology Libretexts
In a double stranded RNA form, retroviruses infect a host cell with their genome, and then are reverse transcribed into double stranded DNA, with the DNA then integrated into the home cell genome When integrated into a host genome, a retrovirus is hard to detect and can lay dormant for prolonged periods, having no discernible effect on the hostDoubleStranded RNA Production of doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) is a part of the coxsackievirus replication cycle It has been shown that dsRNA is able to directly stimulate a dsRNctivated protein kinase (PKR) A major substrate of PKR is the α subunit of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2α)Replication occurs in host cytoplasm and converts ssmRNA to dsgenomic RNA But dsRNA is a kind of molecule that cells do not produce, and eukaryotic hosts have various antiviral systems that detect and inactivate dsRNA To circumvent this defenses, many dsRNA viruses are replicating their RNA inside icosahedral capsids



Title
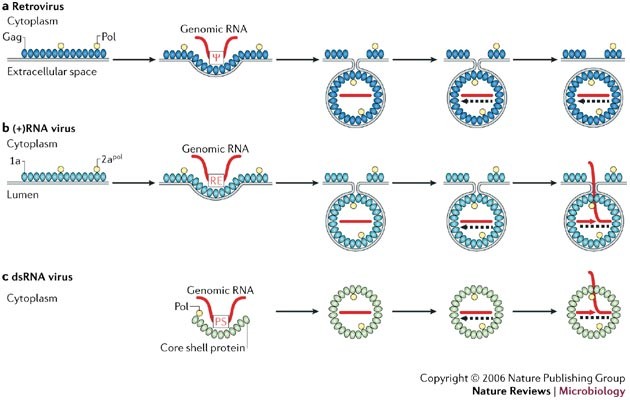



Parallels Among Positive Strand Rna Viruses Reverse Transcribing Viruses And Double Stranded Rna Viruses Nature Reviews Microbiology
1 in a singlestranded RNA virus, a plus strand is one having the same polarity as viral mRNA and containing codon sequences that can be translated into viral protein A minus strand is a noncoding strand that must be copied by an RNAdependent RNA polymerase to produce a translatable mRNA 2 in a singlestranded DNA virus, a plus strand is one contained in the virusDouble stranded RNA, also known as dsRNA, usually shows up in viruses and is somewhat unusual In viruses, it is a unique characteristic, and only a small number of viral families exhibit this trait RNA hybridization happens when one RNA strand combines, or hybridizes, with either another RNA strand or a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) strandAlthough RNA is typically single stranded within cells, there is significant diversity in viruses Rhinoviruses, which cause the common cold;




Negative Strand Rna Virus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
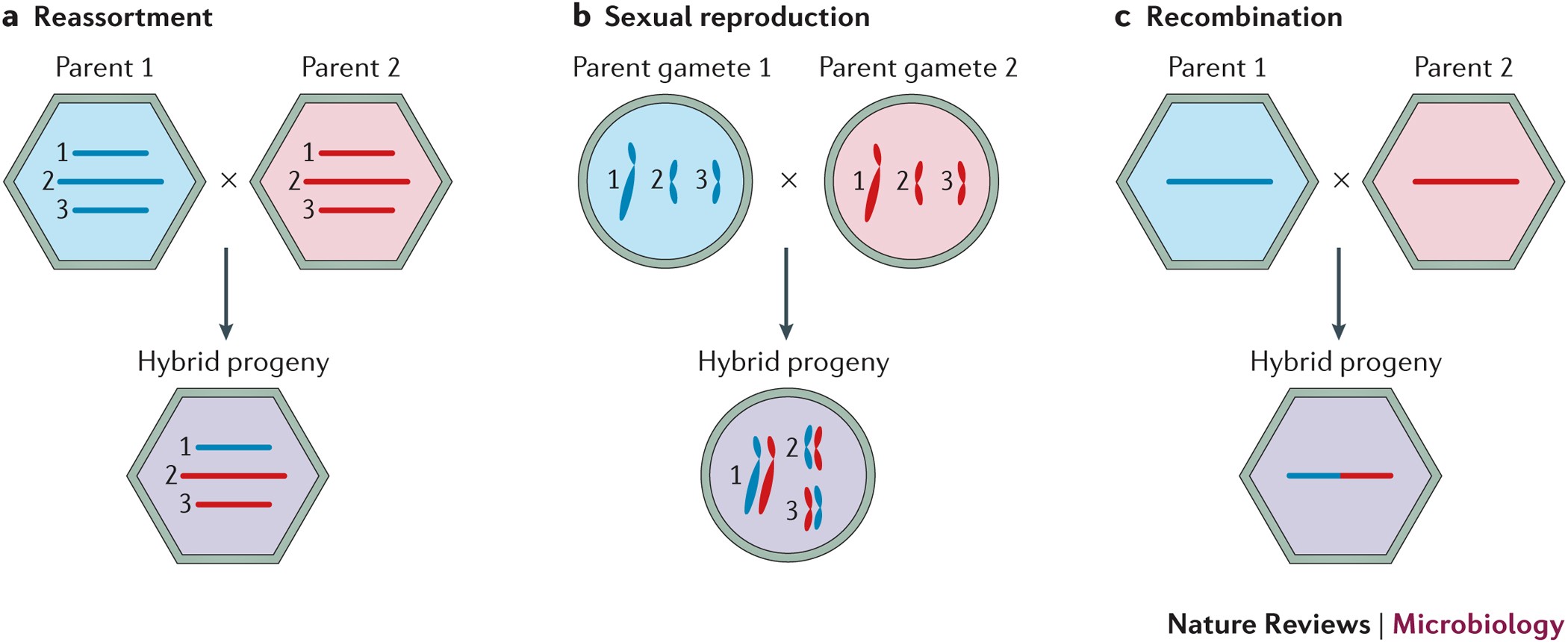



Reassortment In Segmented Rna Viruses Mechanisms And Outcomes Nature Reviews Microbiology
Plant viruses are particles of RNA or DNA that infect plants and cause disease Most plant viruses are singlestranded RNA or doublestranded RNA viruses Common plant viruses include mosaic viruses, spotted wilt viruses, and leaf curl viruses Plant viruses are typically spread by either horizontal or verticle transmissionDoublestranded (ds) RNA viruses are a diverse group of viruses that infect a large range of hosts like animals, bacteria, plants and fungi Members of this group include the rotaviruses, globally known as a common cause of gastroenteritis in kids, and bluetongue virus, an economically damaging pathogen of cattle and sheepT4 virus that attacks EColi Group 3 double stranded RNA Group 3 examples rotovirus Group 4 () single stranded RNA Group 4 examples single stranded RNA / reverse transcription Group 6 expample HIV Group 7 double stranded DNA/reverse transcription Group 7 example Hep B Other sets by this creator Surgical Practice Final exam prep




Availableprotein 3d Structures Of Ssrna And Dsrna Virus Families Download Table




Rna Viruses Polarity Sense Or Sense Size Of Genome Ppt Video Online Download
RNA interference (RNAi) is a genetic regulatory system that functions to silence the activity of specific genes RNAi occurs naturally, through the production of nuclearencoded premicroRNA (premiRNA), and can be induced experimentally, using short segments of synthetic doublestranded RNA (dsRNA)Examples of double stranded RNA viruses Baltimore Class 3 reoviruses How do double stranded RNA viruses replicate Baltimore Class 3?Answer (1 of 6) Adenovirus, herpes virus, poxvirus and papillomavirus are examples of DNA virus Rotavirus, polio virus, yellow fever virus, dengue virus, hepatitis C virus, measles virus, rabies virus, influenza virus and Ebola virus are examples of



The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology



Viral Replication
A virus consists of genetic information — either DNA or RNA — coated by a protein Accordingly, they are classified as DNA viruses and RNA viruses The nucleic acid may be single or double stranded, circular or linear, segmented or unsegmented DNA virusesLater, groups of viruses were classified by the type of nucleic acid they contained, DNA or RNA, and whether their nucleic acid was single or doublestranded However, these earlier classification methods grouped viruses differently, because they were based on different sets of characters of the virus The replication of the positive sense RNA viruses occurs through the doublestranded RNA intermediate Upon infection, the polyproteins encoded for the viral replication are translated The replication of the singlestranded RNA leads to the formation of RNA duplex which in turn is transcribed into singlestranded positive genomic mRNA



Nptel Ac In




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
To remember that REO virus has a doublestranded R NA genome, think " Double R hymes are REO ccuring all the time" "A vegan INFLUENCER ate ( 8 ) 3 BUN nies and upset 10–12 RE aders in 2 ARE as " INFLUENZA virus has 8 segments , BUN yavirus has 3 , RE oviruses has 10–12 , and ARE naviruses has 2 They are the negative or minus (−)strand RNA viruses, the closely related ambisense RNA viruses, and doublestranded RNA viruses (Table 102 and Box 102) For each of these groups of viruses, the first synthetic event after genome penetration isDoublestranded RNA (dsRNA) longer than 30 bp is a key activator of the innate immune response against viral infections It is widely assumed that the generation of dsRNA during genome replication is a trait shared by all viruses However, to our knowledge, no study exists in




Origins And Evolution Of The Global Rna Virome Mbio



Title
Moreover, they cause latent infections Some examples of DNA viruses are Herpes viruses, poxviruses, hepadnaviruses, and hepatitis B What are RNA Viruses? Positivesense singlestranded RNA (ssRNA) viruses are one such way and it is a key aspect of the infectious cycle of the virus Two important examples ofClass VI viruses ssRNART, also called the retroviruses are RNA reverse transcribing viruses with a DNA intermediate Their genomes consist of two molecules of positive sense single stranded RNA with a 5′ cap and 3′ polyadenylated tail Examples of retroviruses include Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Human TLymphotropic virus (HTLV)




Baltimore Classification Wikipedia




Origins And Evolution Of The Global Rna Virome Mbio
This Video will explain about the replication of Double Stranded RNA viruses Detailed Mechanism and Examples will be discussed in Best wayHIV1 is a singlestranded RNA retrovirus that uses reverse transcriptase to create a doublestranded DNA copy of its genome which is integrated into the host human's genome prior to making mRNAs (Group VI) The genome structure system classifies both viruses as singlestranded RNA viruses with linear genomes



Ds Rna Plant Viruses




Positive Strand Rna Viruses In Animals Boundless Microbiology
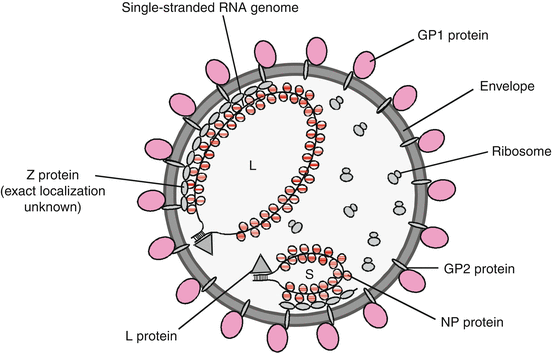



Viruses With Single Stranded Segmented Negative Sense Rna Genomes Springerlink
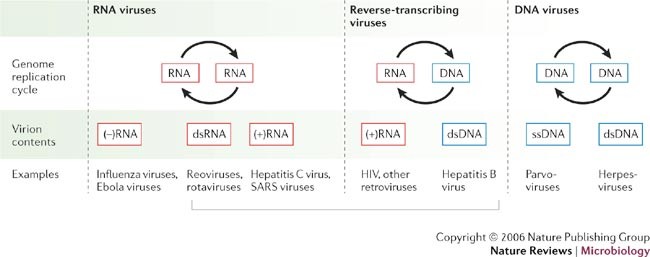



Parallels Among Positive Strand Rna Viruses Reverse Transcribing Viruses And Double Stranded Rna Viruses Nature Reviews Microbiology




Rna Virus Wikipedia




Difference Between Ssrna And Dsrna Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




Viruses Sketchy First Aid Etc Flashcards Quizlet




Dsrna Htrf Kit Cisbio



Replication Of Viruses




Differences Between Dna And Rna Viruses Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
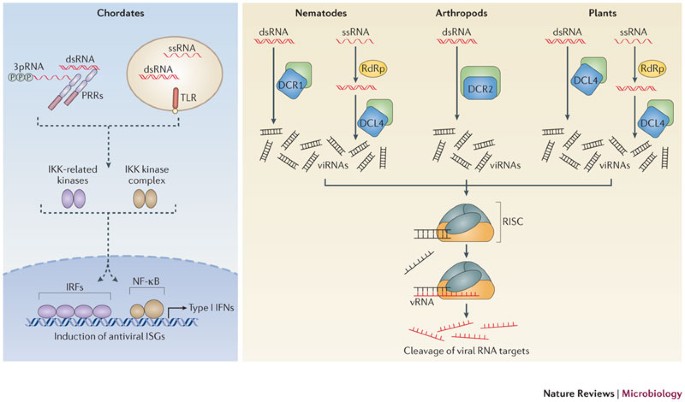



Rna Viruses And The Host Microrna Machinery Nature Reviews Microbiology




Viruses Join The Circular Rna World Tan 21 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library




Double Stranded Rna Viruses These Midpoint Rooted Maximum Likelihood Download Scientific Diagram




Double Stranded Dna Virus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



The Gold Standard In Viral Dsrna Detection Monoclonal J2 K1 K2 Antibodies News Blog Jena Bioscience




Double Membrane Vesicles As Platforms For Viral Replication Trends In Microbiology




Double Stranded Rna Under Force And Torque Similarities To And Striking Differences From Double Stranded Dna Pnas




Virus Structure And Classification Video Khan Academy



1




Programmable Low Cost Dna Based Platform For Viral Rna Detection




Segmented Double Stranded Rna Viruses Structure And Molecular Biology




Host Factors In Positive Strand Rna Virus Genome Replication Journal Of Virology




Positive Strand Rna Viruses In Animals Boundless Microbiology
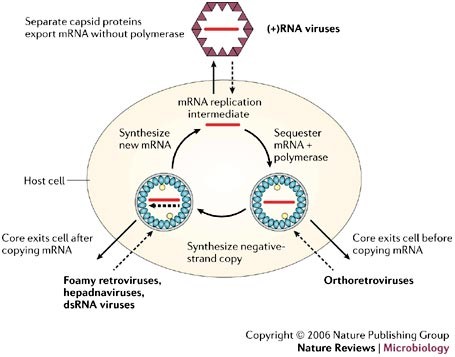



Parallels Among Positive Strand Rna Viruses Reverse Transcribing Viruses And Double Stranded Rna Viruses Nature Reviews Microbiology




Solved 1 Compare And Contrast Dna And Rna Viruses 2 List Chegg Com




Retroviruses Double Stranded Rna Viruses Boundless Microbiology




Coronavirus Endoribonuclease Targets Viral Polyuridine Sequences To Evade Activating Host Sensors Pnas




Cystoviridae Cystoviridae Dsrna Viruses Ictv



1
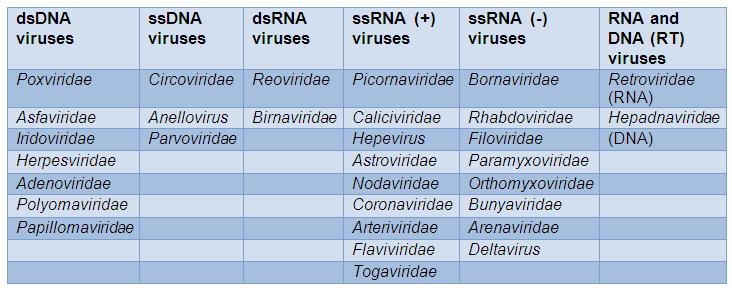



Classification Of Virus Online Biology Notes




Analysis Of Double Stranded Rna From Microbial Communities Identifies Double Stranded Rna Virus Like Elements Sciencedirect




Rig I Detects Viral Genomic Rna During Negative Strand Rna Virus Infection Cell




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Cystoviridae Cystoviridae Dsrna Viruses Ictv
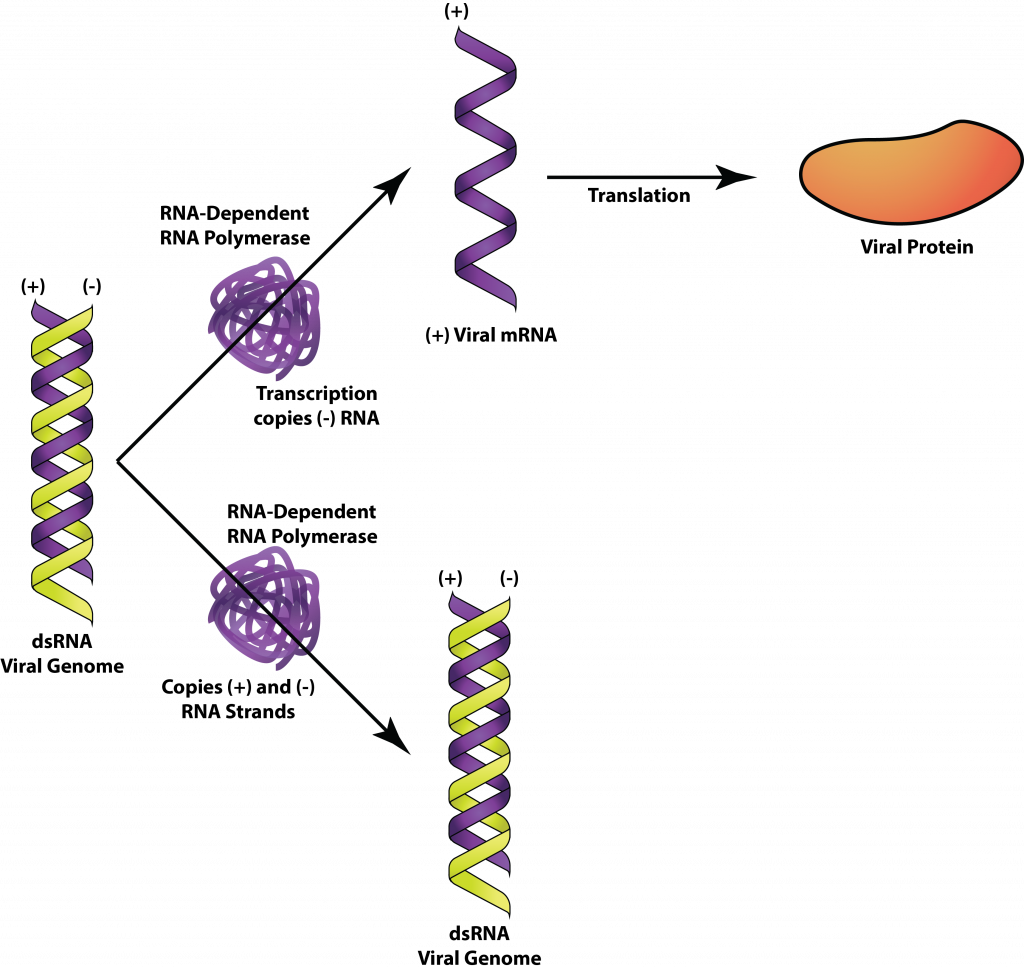



The Viruses General Microbiology




General Virology Knowledge Amboss
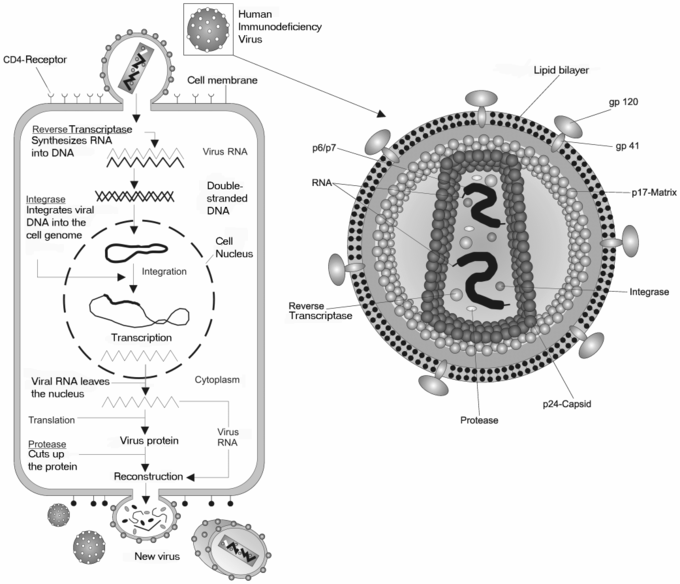



9 10a Double Stranded Rna Viruses Retroviruses Biology Libretexts
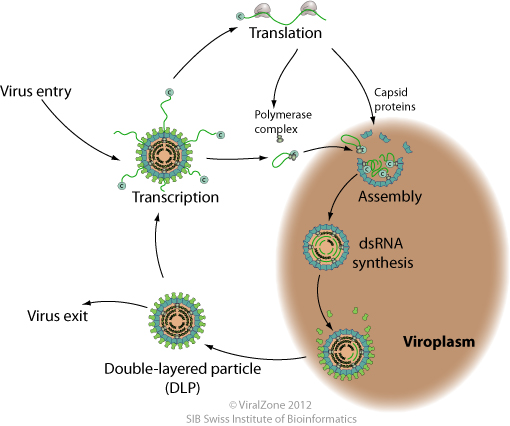



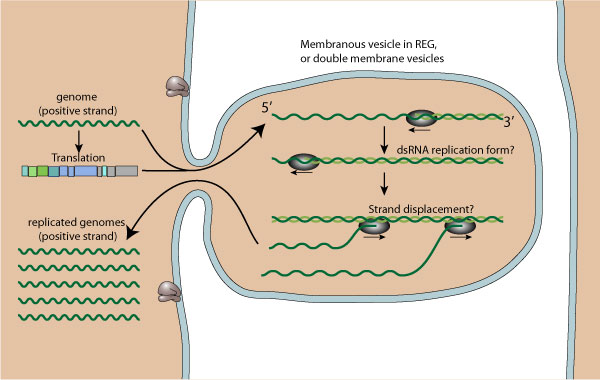
Dsrna Replication Transcription Viralzone



Ppt Double Stranded Rna Viruses Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Viruses Viruses Are Very Small Anatomy Of A Virus Ppt Download




Danielle Blondel Laboratoire De Virologie Molculaire Et Structurale



Viruses Free Full Text Trans Acting Rna Rna Interactions In Segmented Rna Viruses Html



Extraction And Purification Of Large Dsrnas From Virus Infected Plants And Fungi Applications In Virus Detection And Identification
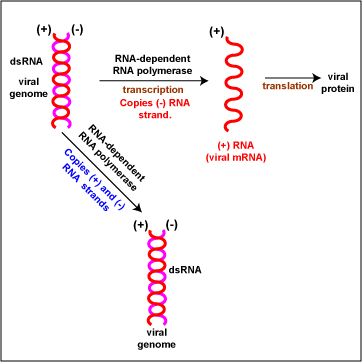



10 4 Classification Of Viruses Biology Libretexts



Reverse Genetics Systems Of Plant Negative Strand Rna Viruses Are Difficult To Be Developed But Powerful For Virus Host Interaction Studies And Virus Based Vector Applications Phytopathology Research Full Text



1




8 Replication Of Positive Stranded Rna Virus Youtube




Availableprotein 3d Structures Of Ssrna And Dsrna Virus Families Download Table




Characteristics Of Double Stranded Rna Viral Genome Insertions In Four Download Scientific Diagram
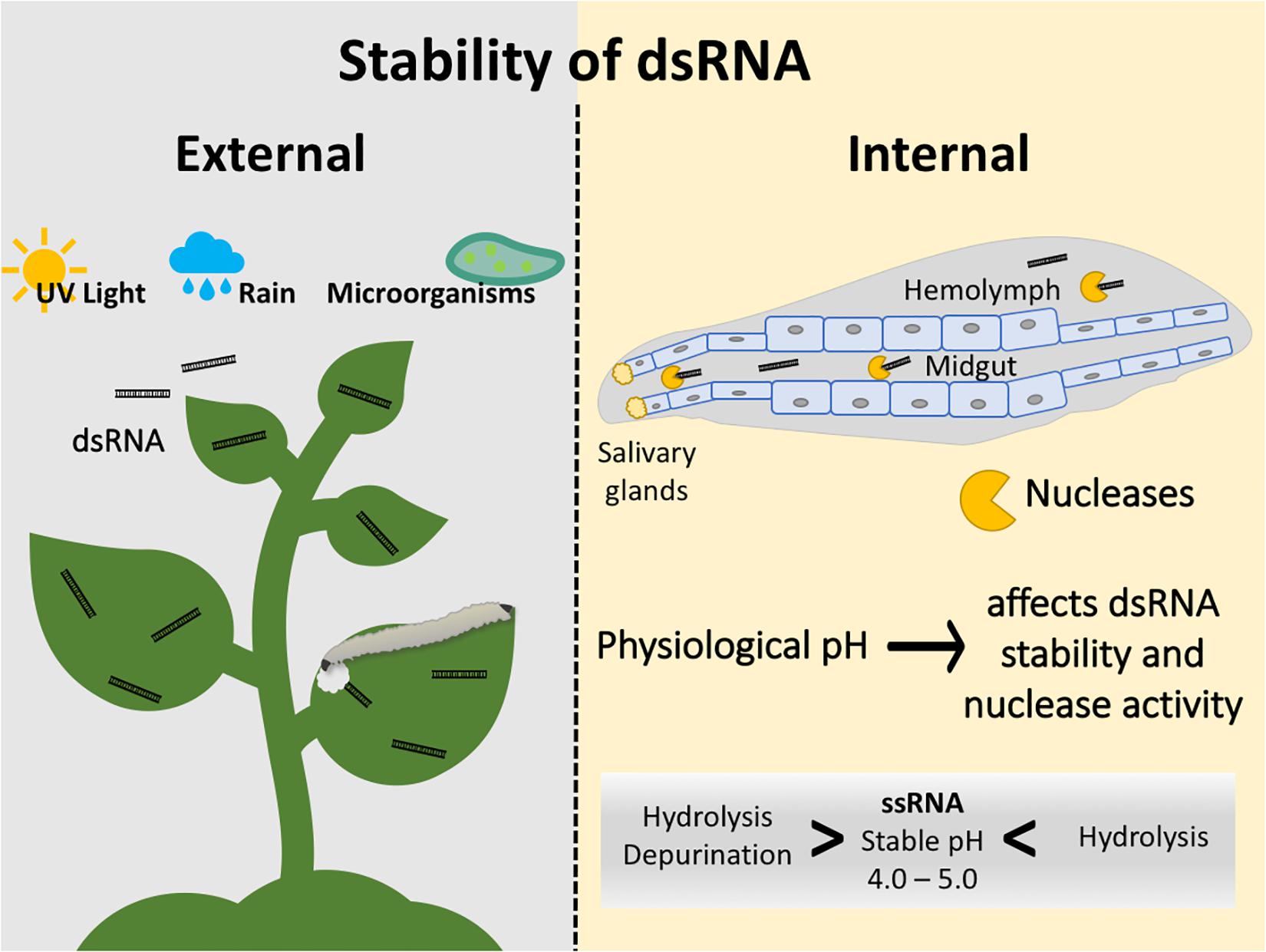



Frontiers Double Stranded Rna Technology To Control Insect Pests Current Status And Challenges Plant Science




Viruses Have Big Impacts On Ecology And Evolution As Well As Human Health The Economist




Rna Virus Replication Transcription Viralzone




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Sars Cov 2 Induces Double Stranded Rna Mediated Innate Immune Responses In Respiratory Epithelial Derived Cells And Cardiomyocytes Pnas
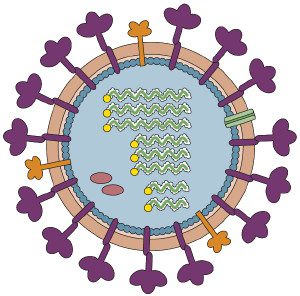



Origin Of Segmented Rna Virus Genomes




Double Stranded Rna Viruses Wikipedia
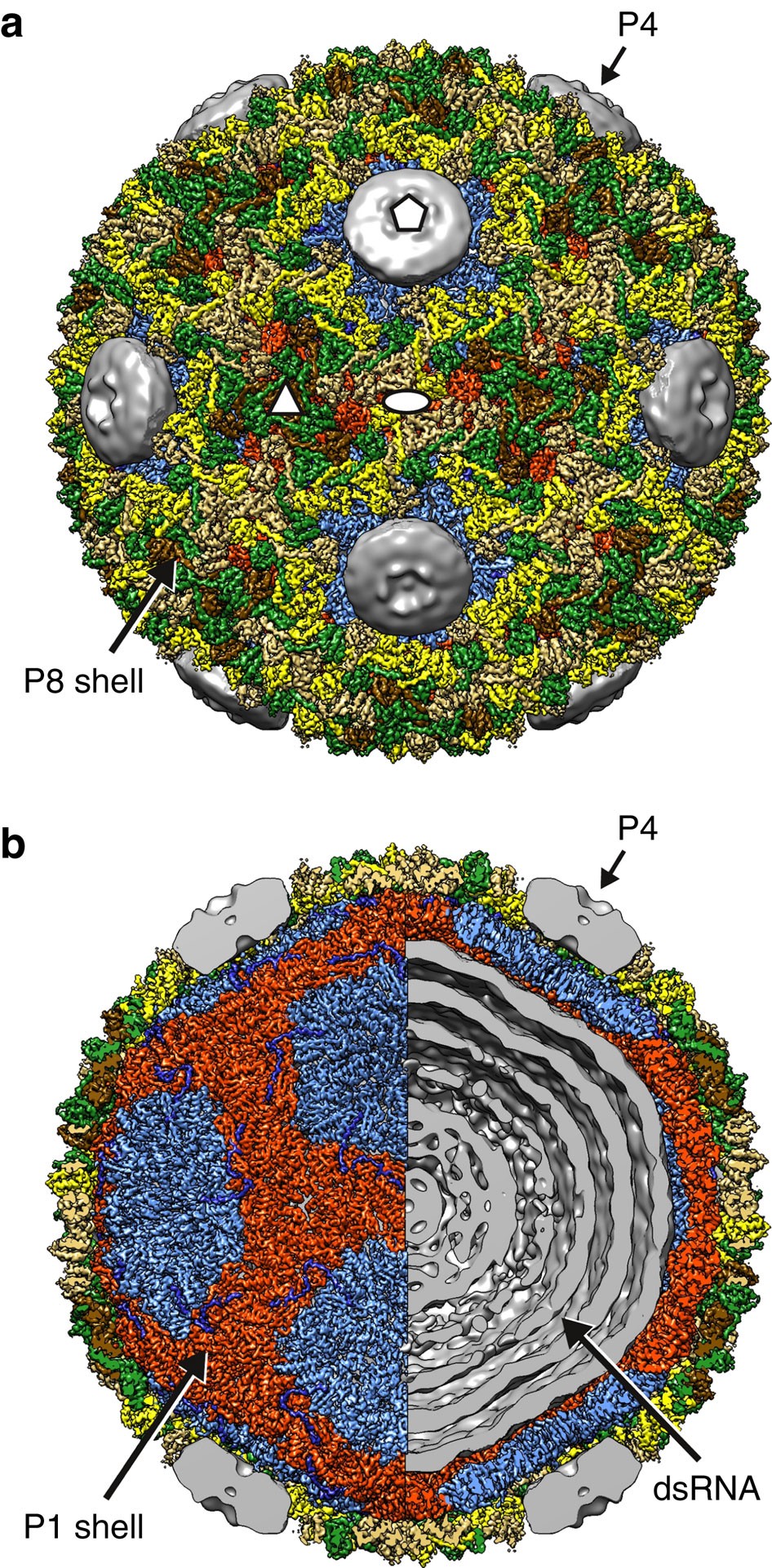



Double Stranded Rna Virus Outer Shell Assembly By Bona Fide Domain Swapping Nature Communications



1




Dna Viruses An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Rna Virus Wikipedia
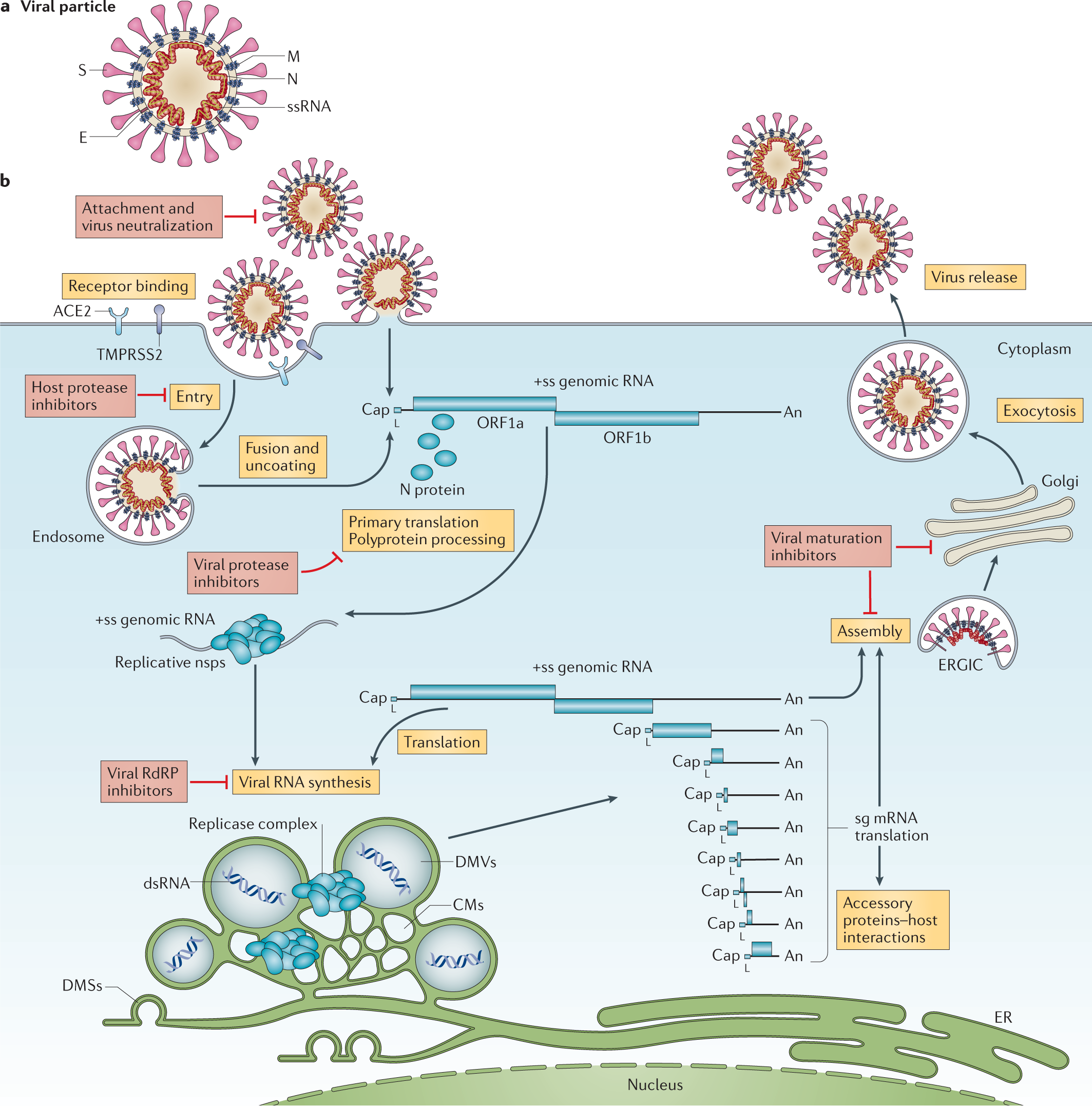



Coronavirus Biology And Replication Implications For Sars Cov 2 Nature Reviews Microbiology




Question About Enveloped Rna Virus Viral Genome Biology Stack Exchange




How To Find If Virus Single Stranded Or Double Stranded Youtube




Viral Genomes Virus A Virus Is A Noncellular




Pdf Parallels Among Positive Strand Rna Viruses Reverse Transcribing Viruses And Double Stranded Rna Viruses Semantic Scholar




Classification Of Medically Important Viruses Review Of Medical Microbiology And Immunology 13th Edition
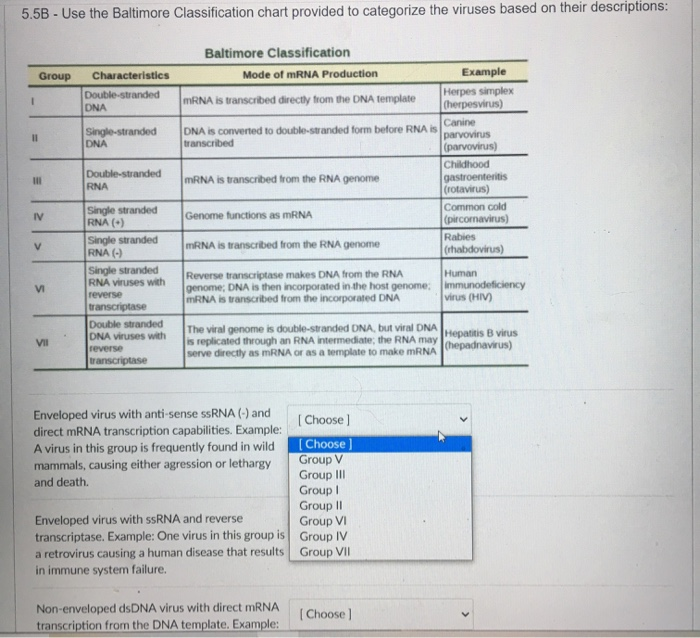



Solved 5 5b Use The Baltimore Classification Chart Chegg Com



P O S I T I V E S I N G L E S T R A N D D N A Zonealarm Results



Title
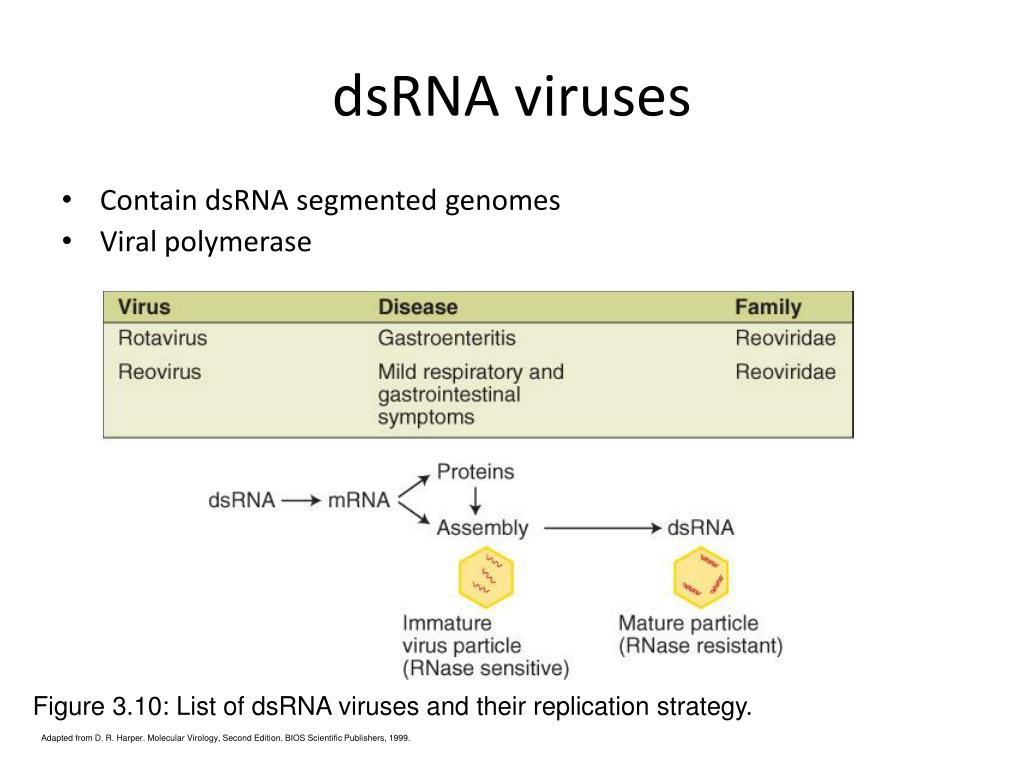



Ppt Rna Viruses Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Double Stranded Rna Virus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Diversity Of Viral Replication Example Of Ebolavirus Versus Download Scientific Diagram




Rna Virus Wikipedia
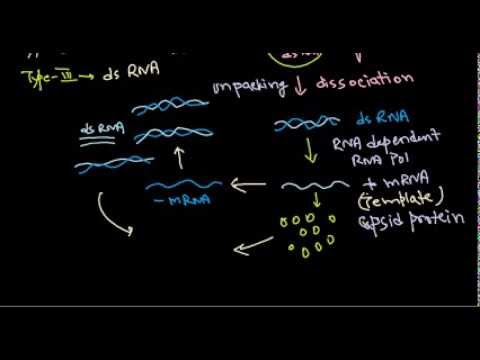



10 Replication Of Dsrna Virus Youtube




How To Find If Virus Genome Rna Or Dna Single Or Double Stranded Youtube
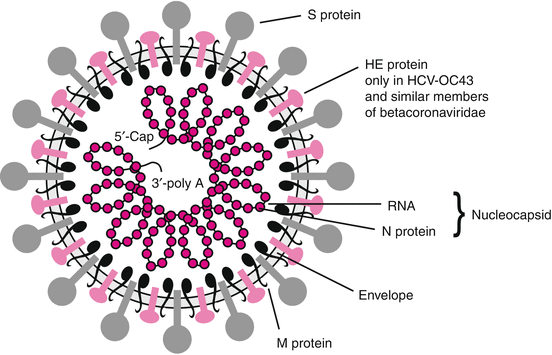



Viruses With Single Stranded Positive Sense Rna Genomes Springerlink
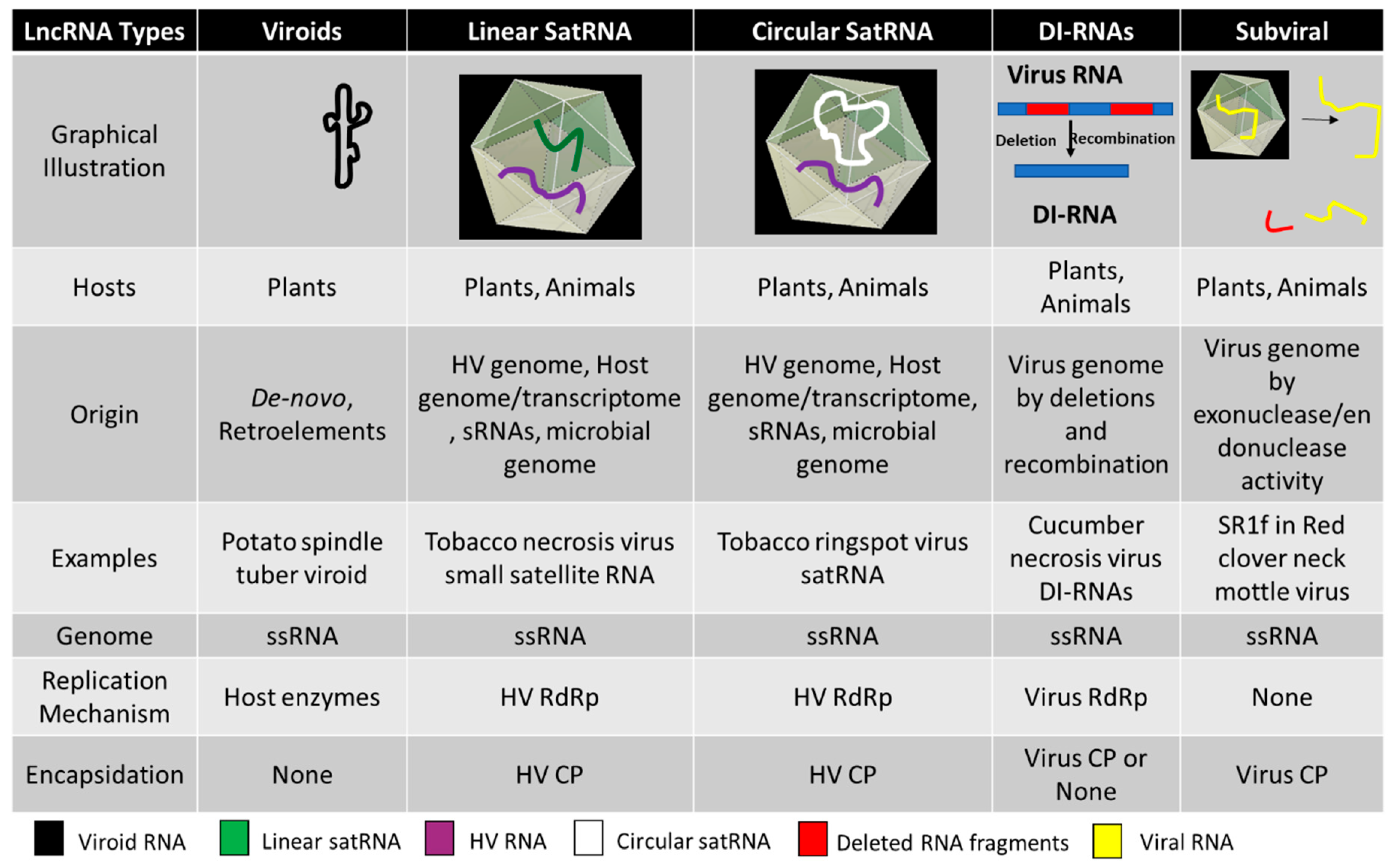



Pathogens Free Full Text Long Noncoding Rnas In Plant Viroids And Viruses A Review Html




Dsrna Htrf Kit Cisbio



Frontiers Exogenous Application Of Rnai Inducing Double Stranded Rna Inhibits Aphid Mediated Transmission Of A Plant Virus Plant Science




Examples Of Zoonotic Rna Viruses Their Known Or Suspected Reservoirs Download Scientific Diagram



Title




22 The Viruses Biology Libretexts




List Of Reported Recombination In Negative Sense Rna Viruses Download Table



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿